A flame is the visible, glowing part of a fire. It is created when a material undergoes combustion, a chemical reaction between a fuel (like wood, gas, or oil) and oxygen, producing heat and light. Flames can have different colors depending on the temperature and the substances being burned.
For example:
- Blue flames indicate complete combustion with high temperatures.
- Yellow or orange flames suggest incomplete combustion with lower temperatures.
- Red flames are usually cooler.
Flames can be categorized based on their combustion characteristics, fuel type, and color. Here are the main types:
1. Based on Combustion
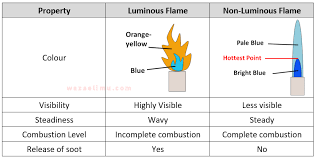
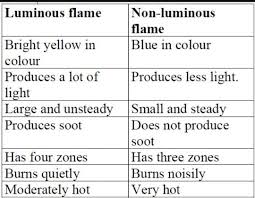
A. Luminous Flame (Yellow Flame)
- Incomplete combustion due to insufficient oxygen.
- Produces soot (unburnt carbon particles).
- Yellow or orange in color.
- Example: Candle flame, gas stove on a low setting.
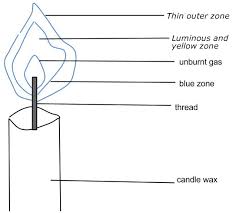
B. Non-Luminous Flame (Blue Flame)
- Complete combustion with sufficient oxygen.
- No soot production, burns cleanly.
- Blue in color and hotter than luminous flames.
- Example: Bunsen burner with open air vents, gas stove on high.
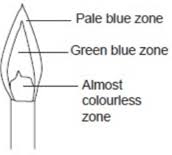
- Different between luminous flame and non luminous flame
2. Based on Fuel Type
A. Solid Fuel Flames
- Occur when burning wood, coal, or paper.
- Produce a mix of yellow, orange, and red flames due to incomplete combustion.
B. Liquid Fuel Flames
- Occur when burning gasoline, alcohol, or kerosene.
- Often produce blue flames with varying intensities.
C. Gas Fuel Flames
- Found in LPG (propane/butane) or natural gas burners.
- Can be either blue (complete combustion) or yellow (incomplete combustion).
3. Based on Temperature and Color
- Red Flames (Lowest temperature, around 600–800°C)
- Orange Flames (Medium temperature, around 1100°C)
- Yellow Flames (Hotter than orange, around 1200°C)
- Blue Flames (Very hot, around 1400–1600°C, complete combustion)
- White Flames (Extremely hot, around 1600–1800°C)
Flames are essential in various aspects of life and technology. Here are some key importance of flames:
1. Daily Life and Cooking
- Used in stoves and ovens for cooking food.
- Essential for heating water and homes in colder regions.
2. Industrial Uses
- Used in welding, metal cutting, and forging.
- Essential in power plants for generating electricity.
- Crucial for burning fuels in engines (e.g., gas turbines, jet engines).
3. Scientific and Laboratory Applications
- Used in Bunsen burners for heating substances in chemistry labs.
- Helps in sterilization of lab equipment.
4. Energy Production
- Flames are used to burn fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas) for energy.
- Used in combustion engines (cars, motorcycles, generators).
5. Safety and Defense
- Fire is used in emergency flares and signal fires.
- Controlled flames are used in firefighting training and rescue operations.
6. Cultural and Religious Significance
- Flames are symbolic in rituals, prayers, and celebrations.
- Used in Olympic torches, candles, and festival lanterns.
7. Environmental and Agricultural Uses
- Helps in controlled burning for forest management.
- Used for waste disposal in incinerators.
Flames have both positive and negative effects, depending on how they are controlled and used.
1. Positive Effects
✔ Energy Production – Flames are essential for generating power in industries, homes, and vehicles.
✔ Cooking and Heating – Used for preparing food and providing warmth in cold climates.
✔ Industrial Applications – Used in welding, metal cutting, and manufacturing.
✔ Scientific Uses – Helps in chemical reactions, sterilization, and laboratory experiments.
✔ Cultural and Religious Significance – Used in ceremonies, rituals, and celebrations.
✔ Agriculture and Waste Disposal – Controlled burning helps in land clearing and waste management.
2. Negative Effects
1.Fire Hazards – Uncontrolled flames can cause house fires, wildfires, and explosions.
2.Air Pollution – Flames produce smoke, carbon monoxide, and other harmful gases.
3.Health Issues – Exposure to flames and smoke can cause burns, respiratory problems, and eye irritation.
4.Environmental Damage – Wildfires destroy forests, wildlife habitats, and contribute to climate change.
5.Property Destruction – Fires can damage homes, businesses, and infrastructure.


0 Comments: