Mar 26, 2025
Mar 23, 2025


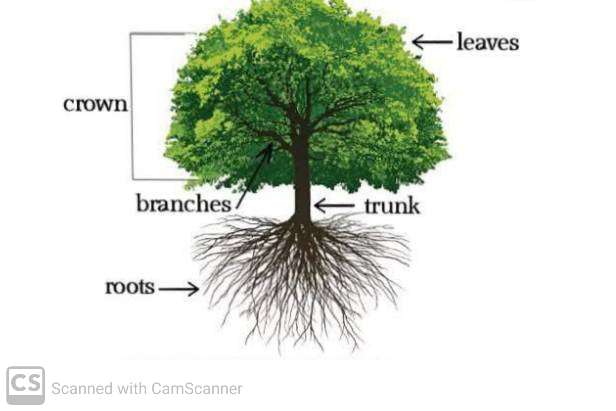




The Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was one of the largest and most powerful empires in West Africa, flourishing between the 15th and 16th centuries. It was centered around the city of Gao, along the Niger River, and expanded to include parts of present-day Mali, Niger, and Nigeria
Factors for the Rise of the Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire became one of the most powerful empires in West Africa between the 15th and 16th centuries. Several factors contributed to its rise and dominance:
1. Strategic Geographical Location
- The empire was centered around Gao, located along the Niger River, which provided fertile land for agriculture, a transportation route, and access to trade networks.
- It controlled key cities like Timbuktu and Djenné, which were major trade and learning centers.
2. Control of Trade Routes
- Songhai dominated the Trans-Saharan trade routes, facilitating trade in gold, salt, ivory, and slaves.
- It became the link between North Africa (Islamic world) and Sub-Saharan Africa, increasing its wealth and power.
3. Strong and Well-Organized Military
- Sunni Ali Ber (1464-1492) built a powerful army with cavalry, infantry, and a navy to protect the empire and expand its territory.
- His military strategies allowed Songhai to conquer important trade cities and consolidate power.
4. Strong Leadership
- Sunni Ali Ber expanded Songhai by capturing Timbuktu (1468) and Djenné (1475), making them part of the empire.
- Askia Muhammad (1493-1528) strengthened administration, promoted Islam, and expanded trade and education.
5. Promotion of Islam and Education
- Askia Muhammad promoted Islamic law (Sharia) and built Islamic schools, mosques, and learning centers.
- Timbuktu became a famous center of Islamic scholarship, attracting scholars from across Africa and the Middle East.
6. Efficient Administrative System
- Askia Muhammad divided the empire into provinces, each governed by an appointed official.
- He introduced a taxation system that generated wealth for the empire.
- Trade regulations ensured economic stability.
7. Agricultural Prosperity
- The fertile Niger River valley supported large-scale agriculture, producing millet, rice, sorghum, and wheat.
- The government promoted irrigation systems to boost food production and support population growth.
8. Alliances and Diplomacy
- The Songhai rulers formed alliances with neighboring kingdoms to secure trade and prevent invasions.
- Askia Muhammad maintained diplomatic relations with North African and Middle Eastern states, strengthening economic and cultural ties.
9. Decline of the Mali Empire
- The decline of the Mali Empire created a power vacuum, allowing Songhai to expand and take control of former Malian territories.
- It took over Mali’s trade routes and cities, boosting its influence.
Conclusion
The rise of the Songhai Empire was driven by geography, strong leadership, military strength, trade dominance, Islam, and an effective administration. These factors helped it become one of the greatest empires in African history before its fall to Moroccan invaders in 1591.

Milima, Aina za Milima, na Faida zake
1. Milima ni nini?
Milima ni miinuko mikubwa ya ardhi inayoinuka juu ya maeneo yanayozunguka. Milima hutofautiana kwa ukubwa, urefu, na muundo wa kijiolojia.
2. Aina za Milima
Milima inaweza kugawanywa katika aina mbalimbali kulingana na jinsi ilivyoundwa:
i) Milima ya Mikunjo (Fold Mountains)
- Hutokea kutokana na mgandamizo wa mabamba ya dunia, ambao husababisha ardhi kuinuka na kujikunja.
- Mfano: Milima ya Himalaya (Asia), Milima ya Alps (Ulaya), Milima ya Andes (Amerika Kusini).

ii) Milima ya Matetemeko (Block Mountains)
- Hutokana na nyufa katika ganda la dunia ambapo sehemu moja inainuka na nyingine inashuka.
- Mfano: Milima ya Vosges (Ufaransa) na Milima ya Ruwenzori (Afrika).

iii) Milima ya Moto (Volcanic Mountains)
- Hutokea kutokana na mlipuko wa volcano ambapo lava na majivu hujikusanya na kuunda milima.
- Mfano: Mlima Kilimanjaro (Tanzania), Mlima Fuji (Japani), Mlima Mauna Loa (Hawaii).

iv) Milima ya Upepo na Mmomonyoko (Residual/ Erosional Mountains)
- Hutokana na mmomonyoko wa ardhi unaosababisha sehemu ngumu za ardhi kubaki kama milima.
- Mfano: Milima ya Ahaggar (Sahara), Milima ya Simien (Ethiopia).

3. Faida za Milima
i) Chanzo cha Maji
- Milima huhifadhi vyanzo vya maji kama mito, chemchemi, na maziwa. Mfano ni Mlima Kilimanjaro, ambao ni chanzo cha mito mingi Tanzania.
ii) Utalii
- Milima huvutia watalii kwa ajili ya kupanda mlima, kuona mandhari nzuri, na shughuli nyingine kama kupiga picha.
iii) Kilimo cha Mteremko
- Milima hutumika kwa kilimo cha mteremko ambacho huzalisha mazao kama chai, kahawa, na ndizi.
iv) Makazi na Utamaduni
- Jamii nyingi huishi milimani na kudumisha tamaduni zao, kama Wamaasai wanaoishi karibu na Milima ya Kenya na Tanzania.
v) Ulinzi wa Mazingira
- Milima huzuia mmomonyoko wa udongo na huchangia katika kuhifadhi bayoanuwai.
vi) Madini na Utajiri wa Maliasili
- Milima ni chanzo cha madini kama dhahabu, almasi, na shaba.
vii) Hali ya Hewa na Mazingira
- Milima husaidia kudhibiti hali ya hewa kwa kuvuta mvua na kupunguza kasi ya upepo.
Kwa ujumla, milima ina umuhimu mkubwa kwa mazingira na binadamu, ikichangia katika uchumi, kilimo, utalii, na uhifadhi wa mazingira.
Mar 22, 2025



Maana ya Mikopo
Mikopo ni kiasi cha pesa au rasilimali kinachotolewa kwa mtu binafsi, kikundi, au shirika kwa masharti ya kurejesha baada ya muda fulani, mara nyingi kwa malipo ya riba. Mikopo hutolewa na taasisi za kifedha kama benki, vikundi vya kijamii, au watu binafsi kwa malengo mbalimbali kama biashara, elimu, au mahitaji ya dharura.
Faida za Mikopo
- Kuongeza Mtaji – Mikopo husaidia watu na biashara kupata fedha za kuendeleza miradi yao.
- Kuwezesha Uwekezaji – Inaruhusu mtu au shirika kuwekeza kwenye mali kama nyumba, ardhi, au mitambo bila kulazimika kusubiri muda mrefu wa kuokoa fedha.
- Kukuza Biashara – Wafanyabiashara hutumia mikopo kupanua biashara zao, kuongeza bidhaa, au kununua vifaa vya kisasa.
- Kuhimiza Maendeleo ya Kijamii – Mikopo ya elimu huwezesha wanafunzi kulipia ada za masomo, na mikopo ya makazi inawasaidia watu kujenga au kununua nyumba.
- Kusaidia Wakati wa Dharura – Inasaidia mtu kukidhi mahitaji ya haraka kama matibabu, ukarabati wa nyumba, au dharura nyinginezo.
Madhara ya Mikopo
- Denikubwa (Madeni Kupindukia) – Kukopa kupita kiasi kunaweza kusababisha mtu au biashara kushindwa kulipa madeni, na hivyo kuingia kwenye matatizo ya kifedha.
- Riba Kubwa – Baadhi ya mikopo huwa na viwango vya juu vya riba, ambavyo vinaweza kuwa mzigo kwa mkopaji.
- Athari kwa Rekodi ya Kifedha – Mtu akishindwa kulipa mikopo kwa wakati, rekodi yake ya kifedha inaweza kuharibika na kupunguza nafasi ya kupata mikopo zaidi siku za usoni.
- Uchukuaji wa Mali – Mikopo yenye dhamana inaweza kusababisha upotevu wa mali kama nyumba au gari endapo mkopaji atashindwa kulipa deni.
- Kujenga Tabia ya Kutegemea Mikopo – Watu au biashara wanaweza kuwa na mazoea ya kutegemea mikopo kila mara badala ya kuokoa au kupanga matumizi vizuri.
Kwa hivyo, mikopo ni chombo muhimu cha kifedha kinachoweza kusaidia maendeleo lakini kinapaswa kutumiwa kwa uangalifu ili kuepuka madhara yanayoweza kutokea.
Mar 21, 2025
Kioo bapa ni aina ya kioo kilichotengenezwa kuwa tambarare, kisicho na makunyanzi wala umbo lolote la ziada. Kioo hiki hutengenezwa kwa kughushi au kukata kioo cha kioo cha kijito (float glass), kisha kukifanya kuwa tambarare na laini ili kiweze kutumika kwa madhumuni mbalimbali.
Kioo bapa hutumika katika maeneo mengi, ikiwa ni pamoja na madirisha, milango ya kioo, samani za kioo, vioo vya magari, na kwenye mapambo ya majengo. Kioo hiki kinaweza kuwa wazi au cha giza kulingana na matumizi yake, na pia kinaweza kufanyiwa matibabu kama kuimarishwa au kupakwa mipako ili kuzuia uharibifu au kuboresha ufanisi wake.
Sifa za Kioo Bapa (Plane Mirror)
1. Uso Laini na Wima – Kioo bapa kina uso laini na tambarare, kinachowezesha kuakisi mwanga kwa utaratibu.
2. Huakisi Mwanga kwa Sheria ya Kuakisiwa – Pembe ya mwanga unaoingia (angle of incidence) ni sawa na pembe ya mwanga unaoakisiwa (angle of reflection).
3. Huunda Picha Halisi ya Mtu au Kitu – Kioo bapa huunda picha inayofanana na kitu halisi lakini inaonekana upande wa kulia na kushoto vikiwa vimebadilishwa (lateral inversion).
4. Picha Inakuwa ya Ukubwa Uleule – Picha inayoundwa na kioo bapa huwa na ukubwa sawa na kitu halisi, bila kupanuliwa au kupunguzwa.
5. Picha Iko Umbali Sawa na Kitu Halisi – Kitu kilicho mbele ya kioo bapa huonekana kwa umbali sawa na umbali wake halisi kutoka kwenye kioo.
6. Picha ni ya Kidhahania (Virtual Image) – Picha haipo katika uhalisia na haiwezi kuakisiwa kwenye skrini.
7. Hutumiwa Sana katika Maisha ya Kila Siku – Kama vile vioo vya nyumbani, magari, maduka, na vifaa vya maabara.
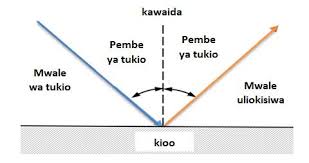
Kuakisiwa kwa mwanga katika kioo bapa
Ni mchakato ambapo mwanga unapogonga uso wa kioo laini na kurudi nyuma bila kupenya ndani ya kioo. Huu ni mfano wa kuakisiwa kwa nuru (reflection of light).
Sheria za Kuakisiwa kwa Mwanga
Kuakisiwa kwa mwanga katika kioo bapa hufuata sheria mbili kuu:
- Mwanga unaoingia (angle of incidence, θi) na mwanga unaoakisiwa (angle of reflection, θr) huwa na pembe sawa kulingana na mstari wa wima kwa uso wa kioo (normal line).
- Hii inamaanisha kuwa θi = θr.
- Mwanga unaoingia, mstari wa wima (normal), na mwanga unaoakisiwa wote wako kwenye ndege moja (same plane).

Aina za Kuakisiwa kwa Mwanga
-
Kuakisiwa kwa Nuru Kawaida (Regular Reflection)
- Hutokea kwenye uso laini kama kioo bapa.
- Mwanga unaoakisiwa huunda picha halisi na ya wazi.
- Hutumika kwenye vioo vya kawaida.
-
Kuakisiwa Kusiko na Mpangilio (Diffuse Reflection)
- Hutokea kwenye nyuso mbaya (zisizo laini).
- Mwanga hutawanyika kwa pembe tofauti, hivyo picha haiundwi vizuri.
- Mfano: Ukuta wa chumba, karatasi, au maji yenye mawimbi.
Matumizi ya Kuakisiwa kwa Mwanga katika Kioo Bapa
Kioo bapa (flat glass) hutumika katika maeneo mbalimbali kutokana na sifa zake za kudumu na uwezo wa kuakisi mwanga. Hapa ni baadhi ya matumizi yake:
1. Madirisha na milango ya kioo – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza madirisha na milango katika nyumba, ofisi, na majengo mengine. Hutoa mwangaza wa asili na mtindo wa kisasa.
2. Vioo vya magari – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza vioo vya magari, kama vile vioo vya mbele, vya pembeni, na vya nyuma.
3. Vioo vya samani – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza sehemu za samani kama vile meza, rafu, na vitabu vya sakafuni.
4. Vioo vya mapambo – Hutumika katika mapambo ya nyumba kama vile taa za kioo, milango ya mapambo, na madirisha ya mapambo.
5. Vioo vya kuakisia – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza vioo vya kuakisia (mirrors), ambayo hutumika katika bafu, vioo vya magari, na maeneo mengine.
6. Vioo vya ujenzi wa majengo – Kioo bapa hutumika katika ujenzi wa majengo ya kibiashara au nyumba za kisasa, ambapo hutumika kama sehemu ya kuta za kioo, vilevile kioo cha makadirio ya mwanga.
7.Vyombo vya sayansi kama periskopu na darubini
Matumizi haya yanahitaji kioo bapa kuwa na ubora wa juu na uwezo wa kustahimili shinikizo na hali ya mazingira

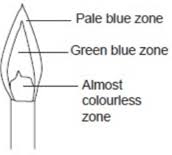
A flame is the visible, glowing part of a fire. It is created when a material undergoes combustion, a chemical reaction between a fuel (like wood, gas, or oil) and oxygen, producing heat and light. Flames can have different colors depending on the temperature and the substances being burned.
For example:
- Blue flames indicate complete combustion with high temperatures.
- Yellow or orange flames suggest incomplete combustion with lower temperatures.
- Red flames are usually cooler.
Flames can be categorized based on their combustion characteristics, fuel type, and color. Here are the main types:
1. Based on Combustion
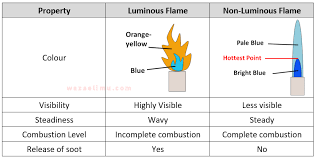
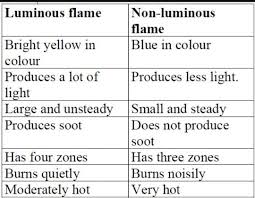
A. Luminous Flame (Yellow Flame)
- Incomplete combustion due to insufficient oxygen.
- Produces soot (unburnt carbon particles).
- Yellow or orange in color.
- Example: Candle flame, gas stove on a low setting.
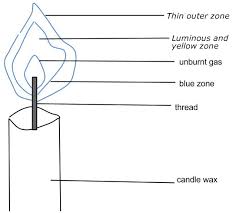
B. Non-Luminous Flame (Blue Flame)
- Complete combustion with sufficient oxygen.
- No soot production, burns cleanly.
- Blue in color and hotter than luminous flames.
- Example: Bunsen burner with open air vents, gas stove on high.
- Different between luminous flame and non luminous flame
2. Based on Fuel Type
A. Solid Fuel Flames
- Occur when burning wood, coal, or paper.
- Produce a mix of yellow, orange, and red flames due to incomplete combustion.
B. Liquid Fuel Flames
- Occur when burning gasoline, alcohol, or kerosene.
- Often produce blue flames with varying intensities.
C. Gas Fuel Flames
- Found in LPG (propane/butane) or natural gas burners.
- Can be either blue (complete combustion) or yellow (incomplete combustion).
3. Based on Temperature and Color
- Red Flames (Lowest temperature, around 600–800°C)
- Orange Flames (Medium temperature, around 1100°C)
- Yellow Flames (Hotter than orange, around 1200°C)
- Blue Flames (Very hot, around 1400–1600°C, complete combustion)
- White Flames (Extremely hot, around 1600–1800°C)
Flames are essential in various aspects of life and technology. Here are some key importance of flames:
1. Daily Life and Cooking
- Used in stoves and ovens for cooking food.
- Essential for heating water and homes in colder regions.
2. Industrial Uses
- Used in welding, metal cutting, and forging.
- Essential in power plants for generating electricity.
- Crucial for burning fuels in engines (e.g., gas turbines, jet engines).
3. Scientific and Laboratory Applications
- Used in Bunsen burners for heating substances in chemistry labs.
- Helps in sterilization of lab equipment.
4. Energy Production
- Flames are used to burn fossil fuels (coal, oil, gas) for energy.
- Used in combustion engines (cars, motorcycles, generators).
5. Safety and Defense
- Fire is used in emergency flares and signal fires.
- Controlled flames are used in firefighting training and rescue operations.
6. Cultural and Religious Significance
- Flames are symbolic in rituals, prayers, and celebrations.
- Used in Olympic torches, candles, and festival lanterns.
7. Environmental and Agricultural Uses
- Helps in controlled burning for forest management.
- Used for waste disposal in incinerators.
Flames have both positive and negative effects, depending on how they are controlled and used.
1. Positive Effects
✔ Energy Production – Flames are essential for generating power in industries, homes, and vehicles.
✔ Cooking and Heating – Used for preparing food and providing warmth in cold climates.
✔ Industrial Applications – Used in welding, metal cutting, and manufacturing.
✔ Scientific Uses – Helps in chemical reactions, sterilization, and laboratory experiments.
✔ Cultural and Religious Significance – Used in ceremonies, rituals, and celebrations.
✔ Agriculture and Waste Disposal – Controlled burning helps in land clearing and waste management.
2. Negative Effects
1.Fire Hazards – Uncontrolled flames can cause house fires, wildfires, and explosions.
2.Air Pollution – Flames produce smoke, carbon monoxide, and other harmful gases.
3.Health Issues – Exposure to flames and smoke can cause burns, respiratory problems, and eye irritation.
4.Environmental Damage – Wildfires destroy forests, wildlife habitats, and contribute to climate change.
5.Property Destruction – Fires can damage homes, businesses, and infrastructure.











 Join Our Telegram Channel
Join Our Telegram Channel
