Msomi Huru is an educational blog that provides clear, insightful, and practical knowledge on academics, society, technology, literature, science, and personal development. Learn freely, grow daily.


Helping others can take many forms, and the best approach often depends on the needs of those around you and your own skills and resources. Here are some ways you can help:
Volunteer: Offer your time to local charities, shelters, or community organizations. This could involve serving meals, tutoring, or participating in cleanup efforts.
Listen: Sometimes, people just need someone to talk to. Being a good listener can provide emotional support and make a significant difference in someone's life.
Share Skills: If you have expertise in a particular area, consider teaching others. This could be anything from cooking and gardening to coding and financial literacy.
Offer Emotional Support: Reach out to friends or family members going through tough times. A simple message or a phone call can show you care.
Donate: If you have the means, consider donating money, clothes, or other goods to those in need.
Advocate: Support causes that aim to help others, whether through awareness campaigns, fundraising, or joining organizations that align with your values.
Be Kind: Small acts of kindness, like holding the door open or complimenting someone, can brighten someone’s day.
Mentor: Offer guidance to someone who may benefit from your experience, whether in a professional setting or personal development.
Create Community: Organize events or groups that bring people together, fostering a sense of belonging and support.
Educate Yourself: Understanding the challenges faced by others can help you be more effective in your efforts to help.
Every small action counts, and your willingness to help can inspire others to do the same!
Racial Association – Africa is home to a large population of Black people, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. This has led some to use "Black Continent" in reference to the majority of the population’s skin color.
Historical Ignorance – In the 19th and early 20th centuries, European explorers and colonizers referred to Africa as the "Dark Continent" because they knew little about its interior. This term reflected their ignorance rather than the reality of Africa's rich and diverse civilizations.
Geographical and Environmental Factors – Some interpretations suggest that "black" could be linked to Africa’s dense forests, volcanic soils, or even the darkness of night in regions with minimal artificial light.
Symbolic Meanings – Some use the term metaphorically to describe Africa’s struggles with colonialism, poverty, and conflict, though this is an oversimplification and does not represent the continent’s full reality.
Today, the term "Black Continent" is not commonly used because it carries colonial and racial connotations. Africa is a diverse continent with rich cultures, histories, and achievements that go beyond such labels.


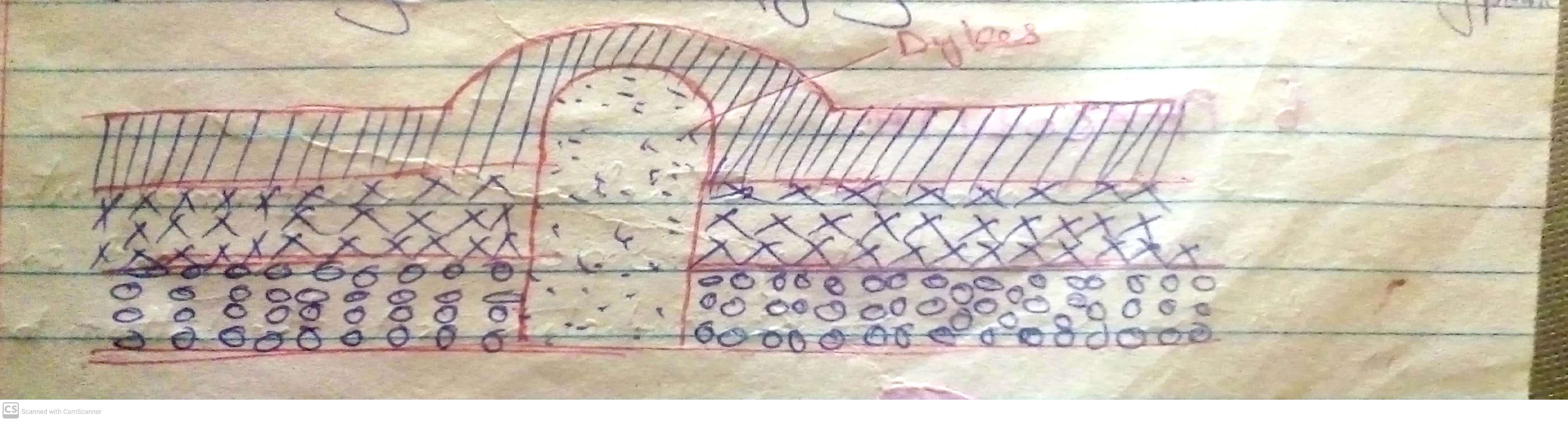

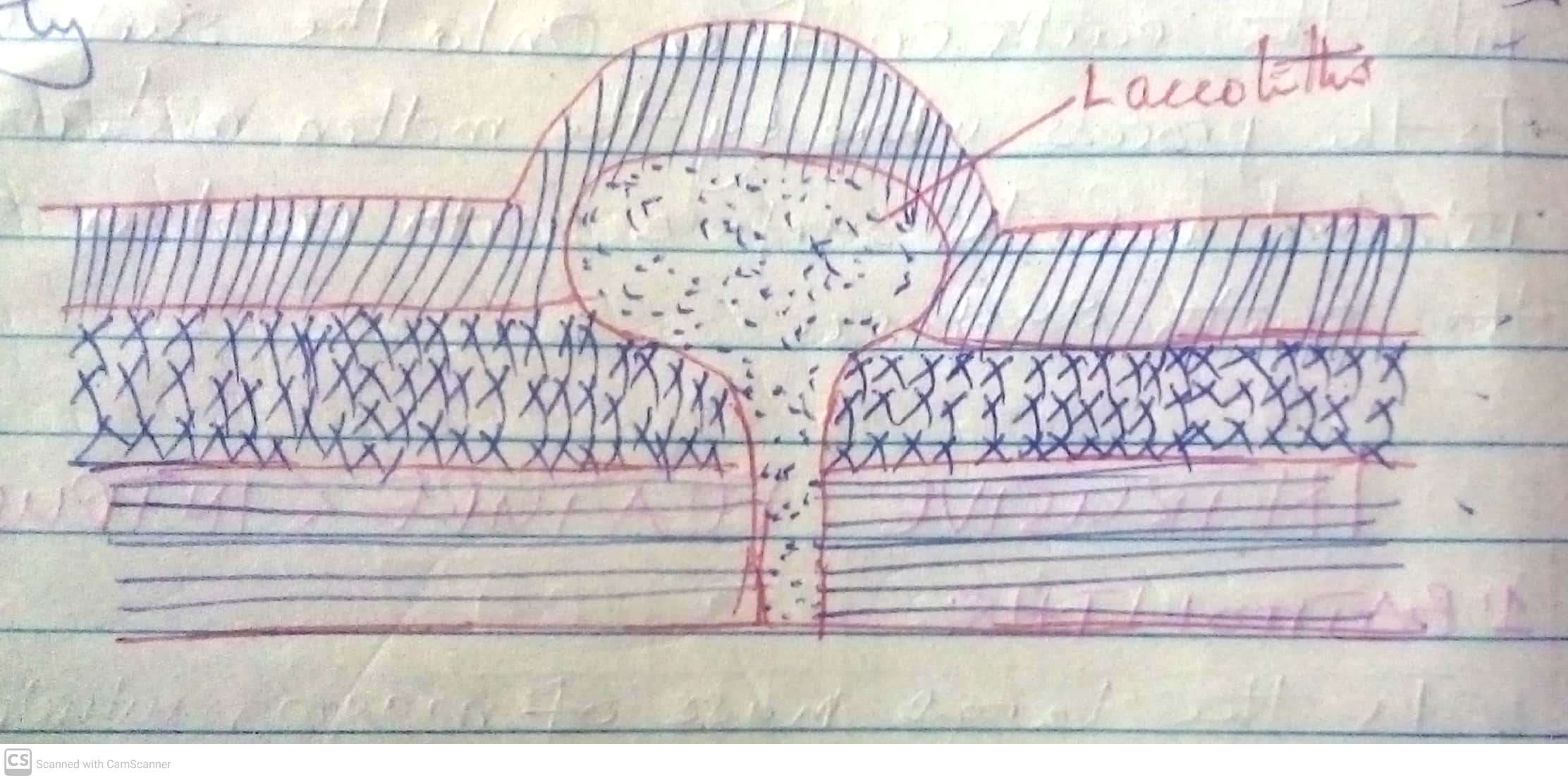
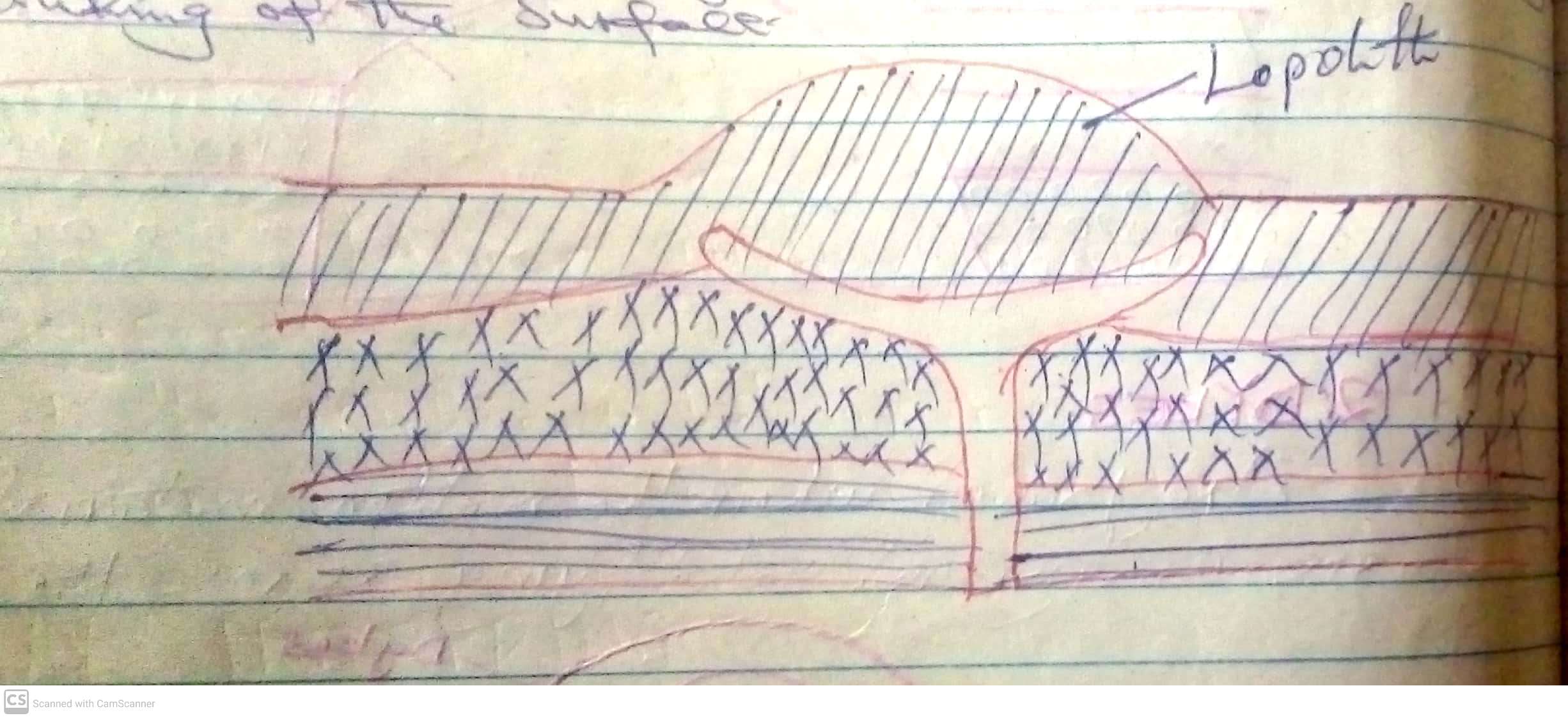

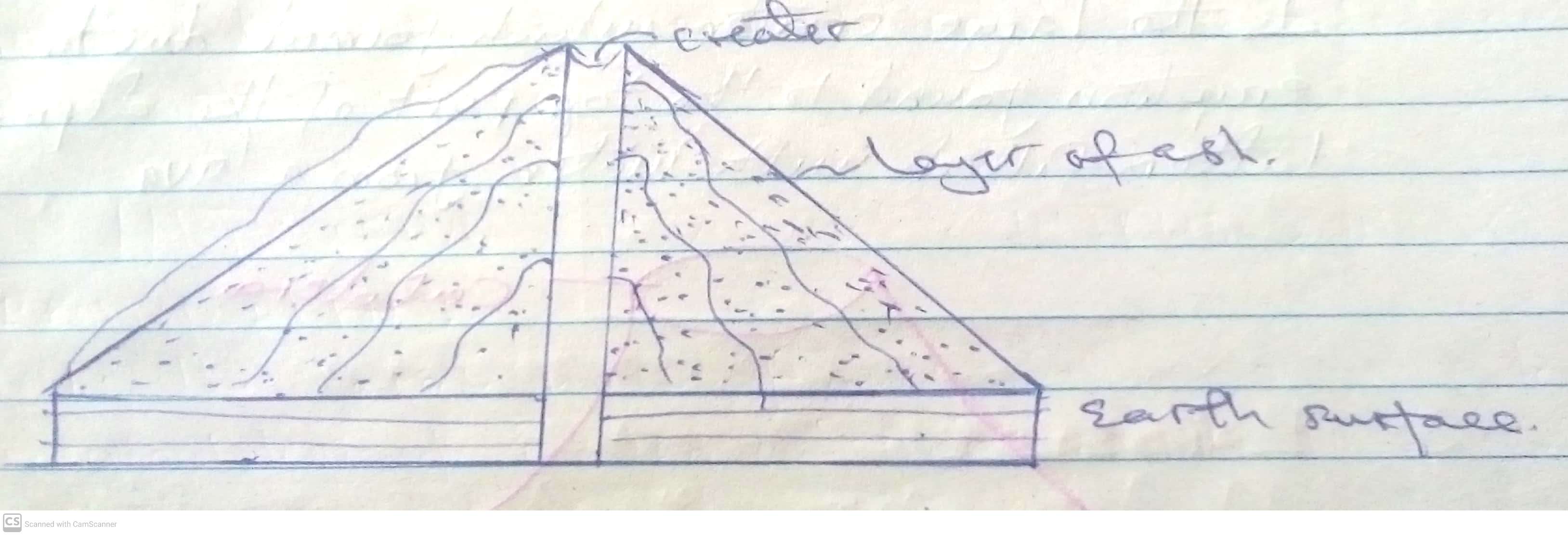

Darasa: Sita
Muda: Dakika 40
Mada: Usanisinuru
Somo: Sayansi na Techolojia
Utangulizi (Dakika 5):
Maelezo ya Dhana (Dakika 10):
Shughuli ya Kivitendo (Dakika 15):
Hitimisho (Dakika 5):
Kazi ya Nyumbani:
Marejeleo:
Mpango huu wa somo unalenga kuwasaidia wanafunzi kuelewa na kuthamini mchakato wa usanisinuru na umuhimu wake katika maisha ya kila siku.
Kwa mawasiliano: Whatsapp no 0768569349
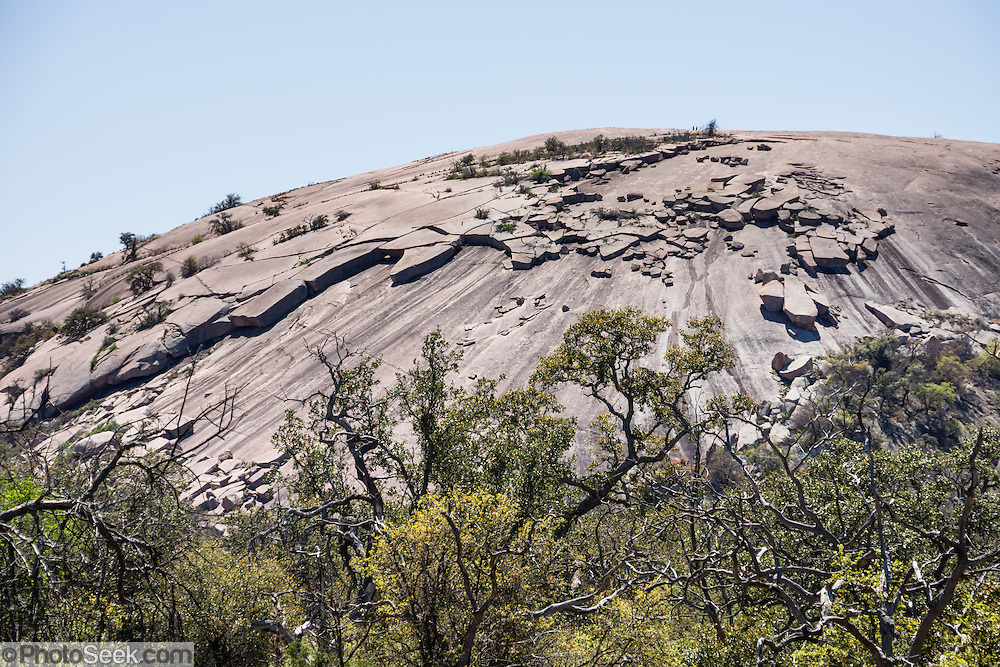
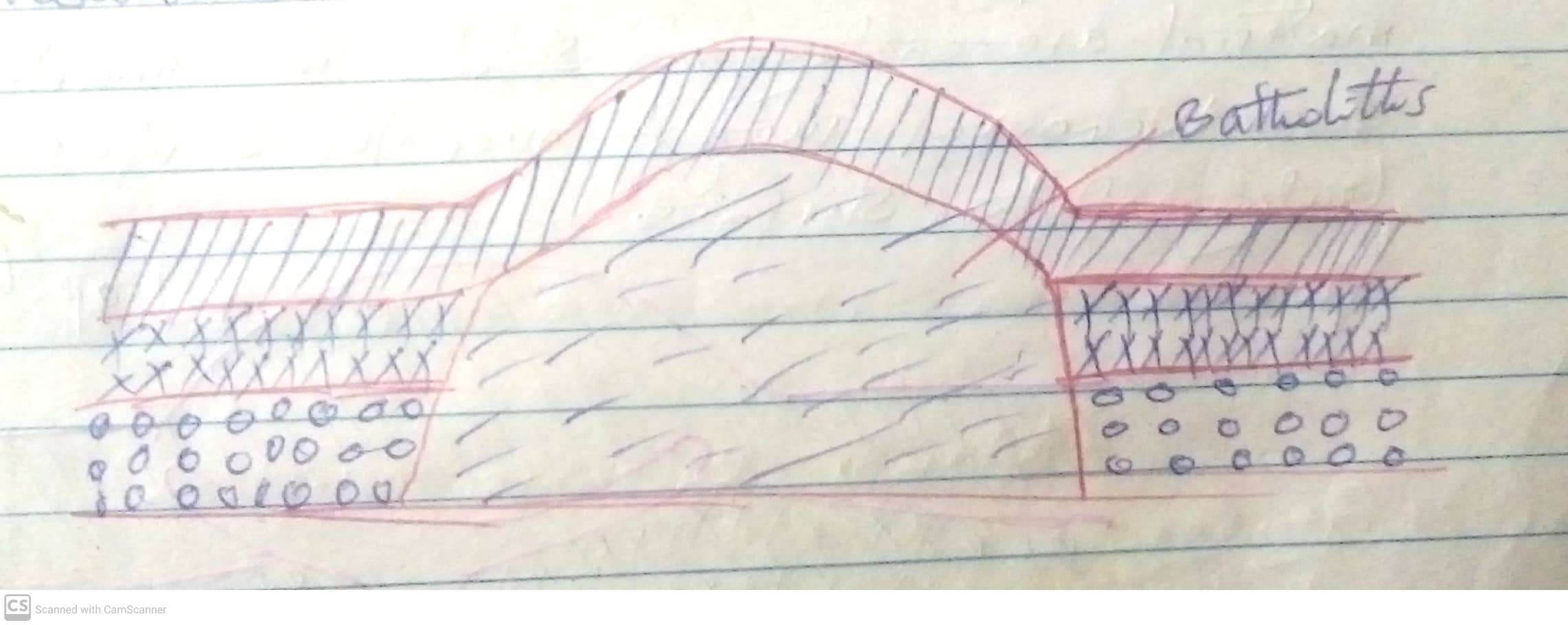
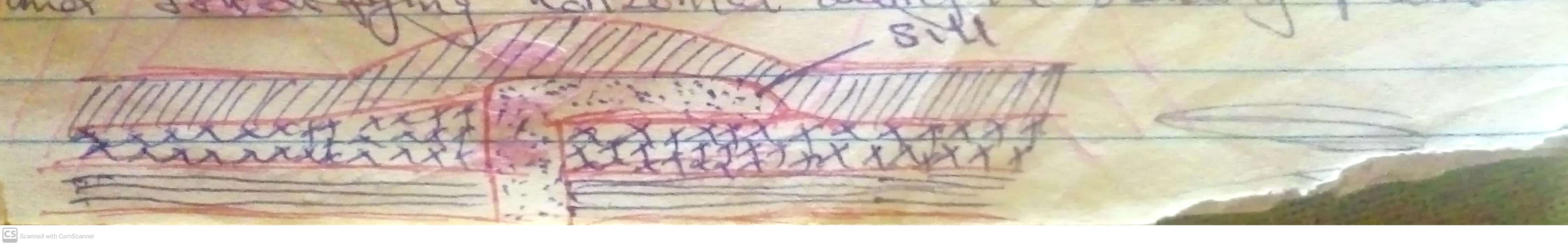
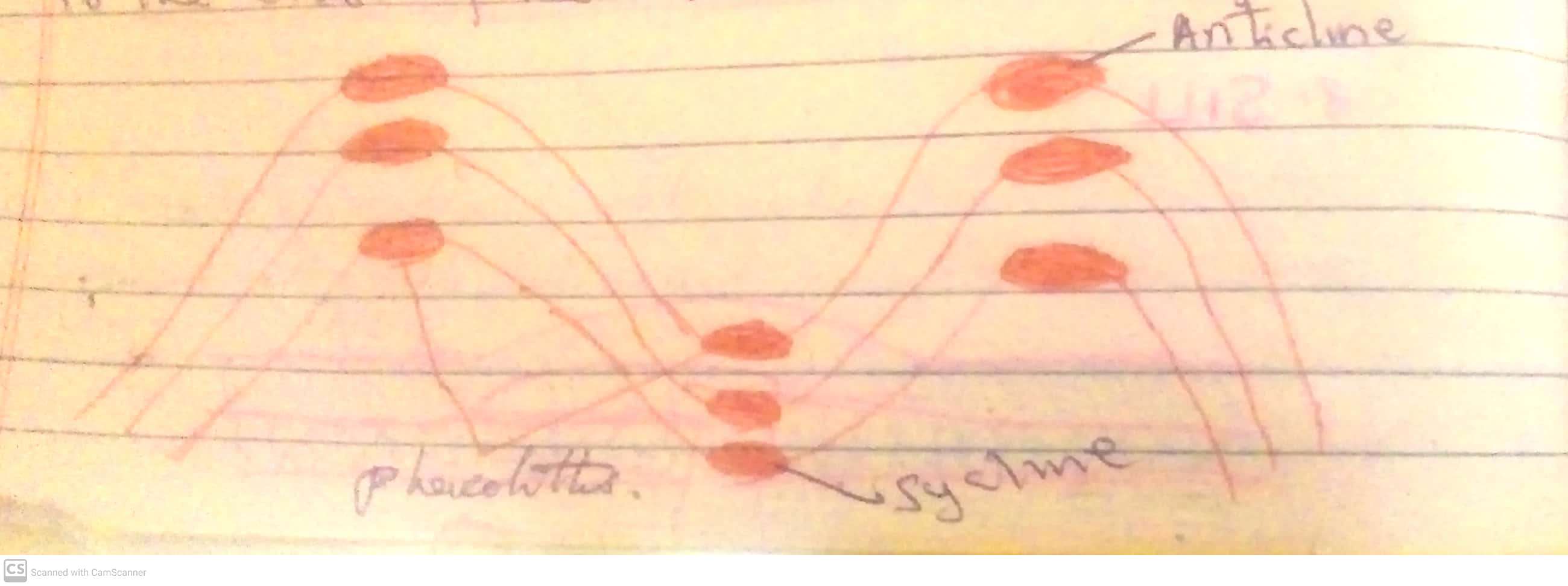
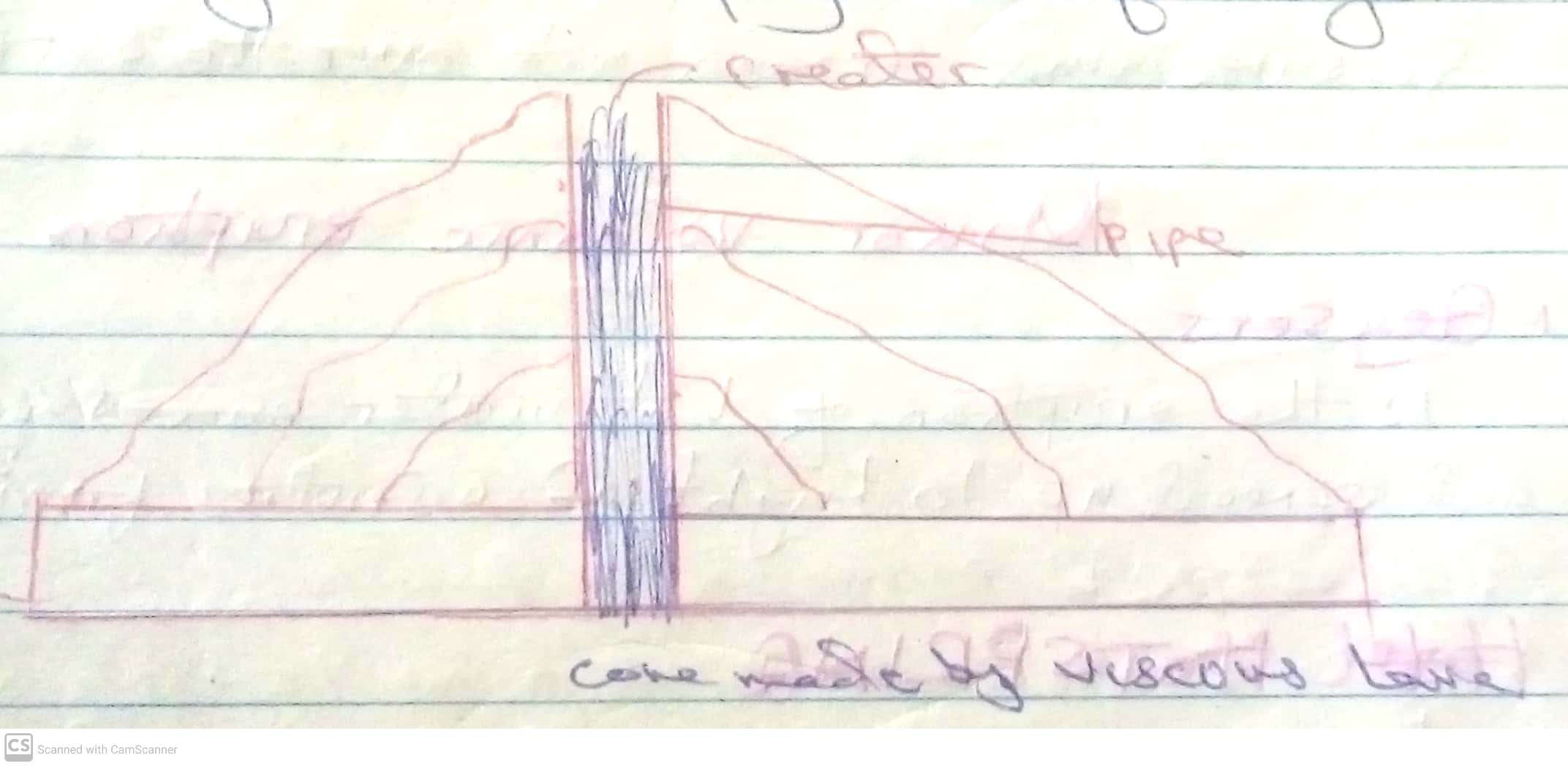
Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest mountain in Africa at 5,895 meters (19,341 feet), is a volcanic mountain located in Tanzania. It consists of three volcanic cones: Kibo (the highest and dormant), Mawenzi, and Shira (both extinct).
Kilimanjaro formed around three million years ago due to volcanic activity caused by the shifting of the East African Rift. Shira was the first to erupt and later collapsed, forming a plateau. Mawenzi and Kibo followed, with Kibo remaining dormant, potentially capable of future eruptions.