Weathering is the physical or chemical disintegration of rock at the earth surface. Weathering can be classified into three type.
TYPES OF WEATHERING
1. Mechanical weathering
2. Chemical weathering
3. Biological weathering
1. MECHANICAL WEATHERING (PHYSICAL)
Is the physical disintegration and reduction in the size of the rock without changing their chemical composition. Example exfoliation, temperature change.
2. MECHANICAL WEATHERING
Is the decomposition or weakness of the rock through chemical process to form residual material example. Oxidation
*Oxidation is reaction of iron element with water and to form rust then reddis the disintegration of rock itself.
3. BIOLOGICAL WEATHERING
Is the disintegration or decay of rock and minerals caused by chemical or physical agent of organism.
Example: Rock disintegration by plant or root growth and acidic secretion.
- Plant penetrate into cracks and crevices of rock and cause the rock split or break into smaller particles through chemical weathering
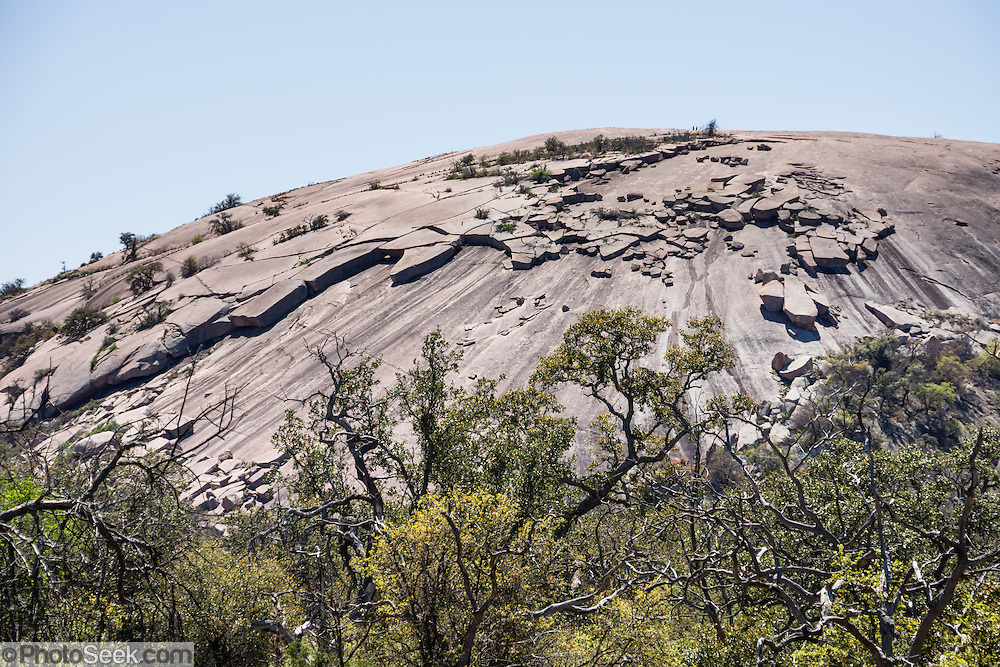

- Erosion:is the physical removal and transportation of weathered material by water,wind,ice, gravity
- Deposition (deposit):is the process by which weathered land eroded material are laid down or place in location that is from different from their source.
IMPORTANT OF WEATHERING
1. Source of land fertility
2. Tourist attraction
3. Creation of new features of rock
EFFECT OF WEATHERING
1. Damage of property
2. Loss of life(death)
DIFFERENTIAL WEATHERING
- Rate are controlled by the type of weathering process and rock material
- Harder rock typically weather slower than soft rock in the same environment
- The differences in the rate of weathering due to rock type or other characteristic is called differential weathering
FEATURES FORMED UNDER WIND EROSION
1. YADANGS: Yardangs are fascinating geological formations sculpted by wind erosion, typically found in desert environments.
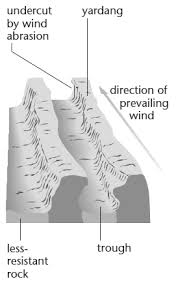
Here are some key points about yardangs:
### **Formation Process**
- **Wind Erosion**: Yardangs are formed by the persistent action of wind erosion. The wind carries particles that abrade the softer rock, leaving behind the harder, more resistant material.
- **Shape**: They are characterized by their elongated shape and steep sides, often aligned parallel to the prevailing wind direction.
### **Types and Sizes**
- **Mega-Yardangs**: These can be several kilometers long and hundreds of meters high, found in arid regions with strong winds.
- **Meso-Yardangs**: Generally a few meters high and 10 to 15 meters long, commonly found in semiconsolidated playa sediments.
- **Micro-Yardangs**: Only a few centimeters high, formed in softer materials.
### **Examples**
- **Qaidam Desert, China**: Known for its extensive yardang fields.
- **Mojave Desert, USA**: Another region where yardangs are prominently found.
### **Significance**
- **Geological Indicators**: Yardangs provide valuable information about past climatic conditions and wind patterns.
- **Tourist Attractions**: Their unique shapes and formations make them popular spots for tourists and photographers.
2. ZEUGENS: Zeugens are fascinating geological formations found in desert environments, created by the combined action of wind erosion and weathering.
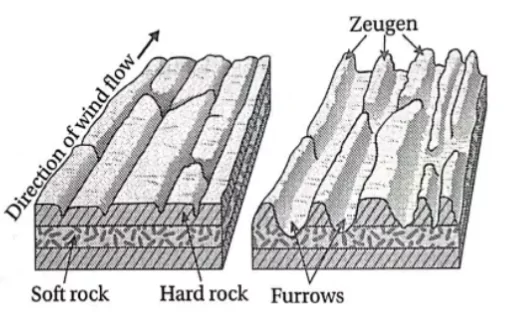
Here are some key points about zeugens:
### **Formation Process**
- **Differential Erosion**: Zeugens form when layers of hard rock overlay softer rock. Wind erosion and weathering processes erode the softer rock more quickly, leaving behind ridges of the harder rock.
- **Ridge and Furrow Landscape**: This differential erosion creates a landscape of alternating ridges (zeugens) and furrows.
### **Characteristics**
- **Height and Length**: Zeugens can vary in height, sometimes reaching up to 30 meters, and can be several meters long.
- **Shape**: They often have a flat, table-like appearance due to the erosion of the softer rock beneath the harder cap rock.
### **Examples**
- **Sahara Desert**: Zeugens are commonly found in the Sahara Desert, where the harsh desert winds and temperature fluctuations contribute to their formation.
- **Namib Desert**: Another region where zeugens are prominently found.
### **Significance**
- **Geological Indicators**: Zeugens provide valuable information about past climatic conditions and wind patterns in desert regions.
- **Tourist Attractions**: Their unique shapes and formations make them popular spots for tourists and photographers.
3. ROCK PEDESTAL:A rock pedestal, also known as a mushroom rock, is a naturally occurring rock formation that looks like a tall, thin column with a wider top, resembling a mushroom. These formations are the result of differential weathering and erosion processes.
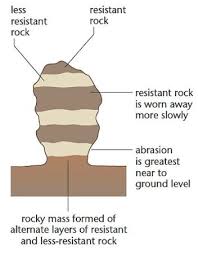
### **Formation Process**
1. **Differential Weathering**: The rock pedestal forms when the softer rock at the base erodes faster than the harder rock on top. This differential weathering occurs due to the varying resistance of rock layers to weathering agents like wind, water, and temperature changes.
2. **Erosional Forces**: Wind abrasion and water erosion play significant roles in shaping the pedestal. The wind carries particles that abrade the softer rock at the base, while water runoff can further erode the lower parts.
3. **Stability**: The harder, more resistant rock at the top protects the softer rock beneath it from weathering, creating the distinctive mushroom shape.
### **Examples**
- **The Yardangs**: Found in desert regions, these elongated rock formations are often accompanied by rock pedestals.
- **Goblin Valley State Park, Utah**: Known for its numerous mushroom rock formations, shaped by wind and water erosion.
### **Significance**
- **Geological Indicator**: Rock pedestals provide valuable information about the geological history and environmental conditions of the region where they are found.
- **Tourist Attractions**: These unique formations are often popular tourist spots, attracting visitors and photographers.
Rock pedestals showcase the power of natural erosional processes and stand as striking features in various landscapes around the world.


0 Comments: