The origin of humans is a fascinating and complex topic that spans millions of years. Human evolution is the process by which modern humans, Homo sapiens, developed from our ancient ancestors. Here are some key points:
1. **Early Primates**: The evolutionary history of primates, the group that includes humans, dates back about 65 million years. Early primates evolved in tropical forests and gradually developed traits like grasping hands and forward-facing eyes.
2. **Hominins**: Around 6 to 7 million years ago, the lineage that would lead to humans diverged from the one that led to chimpanzees and bonobos. These early ancestors are known as hominins¹.
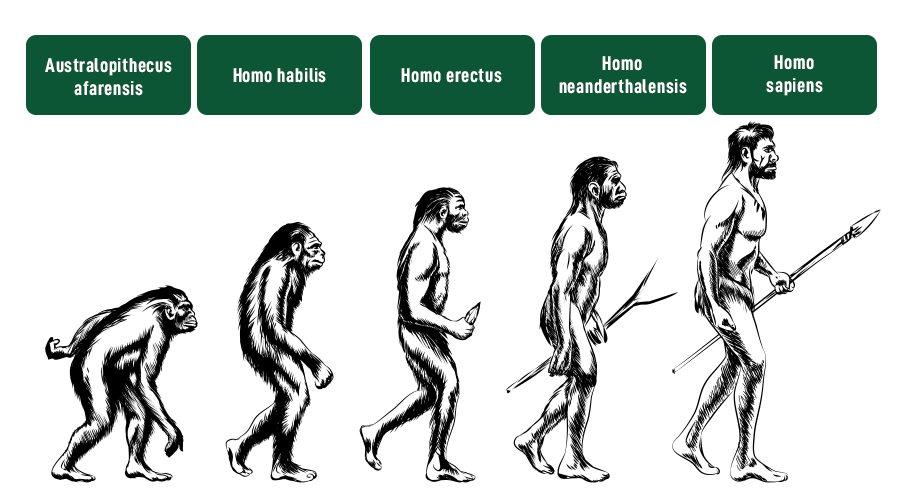
3. **Australopithecines**: One of the most famous early hominins is Australopithecus, which lived between 4 and 2 million years ago. These species were bipedal, meaning they walked on two legs, but still had many ape-like features¹.
4. **Genus Homo**: The genus Homo, which includes modern humans, appeared around 2.8 million years ago. Early members of this genus, such as Homo habilis, were known for their use of simple stone tools².
5. **Homo sapiens**: Anatomically modern humans, Homo sapiens, emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago. Over time, they developed complex language, art, and technology, and eventually spread across the globe².
6. **Interbreeding**: Modern humans also interbred with other hominin species, such as Neanderthals and Denisovans, which contributed to the genetic diversity seen in humans today².
The study of human evolution involves multiple scientific disciplines, including anthropology, paleontology, and genetics, to piece together the story of our origins.
Studying the origin of humans is important for several reasons:
1. **Understanding Human Evolution**: It helps us understand the biological and cultural evolution of our species. By studying fossils, artifacts, and genetic data, we can trace the development of human traits and behaviors over millions of years.
2. **Medical Insights**: Knowledge of human evolution can provide insights into modern human health. For example, understanding the evolutionary history of diseases and genetic disorders can help in developing treatments and preventive measures.
3. **Cultural Awareness**: It fosters a deeper appreciation of human diversity and cultural heritage. By learning about the different paths our ancestors took, we can better understand and respect the variety of cultures and traditions that exist today.
4. **Environmental Adaptation**: Studying how early humans adapted to different environments can inform current efforts to address climate change and environmental challenges. It shows how humans have historically responded to changing conditions and can guide future strategies.
5. **Scientific Curiosity**: It satisfies our innate curiosity about where we come from and how we fit into the natural world. This knowledge enriches our understanding of life on Earth and our place in the universe.
6. **Interdisciplinary Connections**: The study of human origins connects various scientific disciplines, including anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and paleontology. This interdisciplinary approach fosters collaboration and innovation across fields.
7. **Ethical and Philosophical Questions**: It raises important ethical and philosophical questions about what it means to be human. Exploring our origins can lead to deeper reflections on human nature, morality, and our responsibilities to each other and the planet.


0 Comments: