Kioo bapa ni aina ya kioo kilichotengenezwa kuwa tambarare, kisicho na makunyanzi wala umbo lolote la ziada. Kioo hiki hutengenezwa kwa kughushi au kukata kioo cha kioo cha kijito (float glass), kisha kukifanya kuwa tambarare na laini ili kiweze kutumika kwa madhumuni mbalimbali.
Kioo bapa hutumika katika maeneo mengi, ikiwa ni pamoja na madirisha, milango ya kioo, samani za kioo, vioo vya magari, na kwenye mapambo ya majengo. Kioo hiki kinaweza kuwa wazi au cha giza kulingana na matumizi yake, na pia kinaweza kufanyiwa matibabu kama kuimarishwa au kupakwa mipako ili kuzuia uharibifu au kuboresha ufanisi wake.
Sifa za Kioo Bapa (Plane Mirror)
1. Uso Laini na Wima – Kioo bapa kina uso laini na tambarare, kinachowezesha kuakisi mwanga kwa utaratibu.
2. Huakisi Mwanga kwa Sheria ya Kuakisiwa – Pembe ya mwanga unaoingia (angle of incidence) ni sawa na pembe ya mwanga unaoakisiwa (angle of reflection).
3. Huunda Picha Halisi ya Mtu au Kitu – Kioo bapa huunda picha inayofanana na kitu halisi lakini inaonekana upande wa kulia na kushoto vikiwa vimebadilishwa (lateral inversion).
4. Picha Inakuwa ya Ukubwa Uleule – Picha inayoundwa na kioo bapa huwa na ukubwa sawa na kitu halisi, bila kupanuliwa au kupunguzwa.
5. Picha Iko Umbali Sawa na Kitu Halisi – Kitu kilicho mbele ya kioo bapa huonekana kwa umbali sawa na umbali wake halisi kutoka kwenye kioo.
6. Picha ni ya Kidhahania (Virtual Image) – Picha haipo katika uhalisia na haiwezi kuakisiwa kwenye skrini.
7. Hutumiwa Sana katika Maisha ya Kila Siku – Kama vile vioo vya nyumbani, magari, maduka, na vifaa vya maabara.
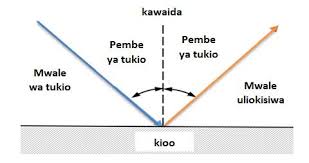
Kuakisiwa kwa mwanga katika kioo bapa
Ni mchakato ambapo mwanga unapogonga uso wa kioo laini na kurudi nyuma bila kupenya ndani ya kioo. Huu ni mfano wa kuakisiwa kwa nuru (reflection of light).
Sheria za Kuakisiwa kwa Mwanga
Kuakisiwa kwa mwanga katika kioo bapa hufuata sheria mbili kuu:
- Mwanga unaoingia (angle of incidence, θi) na mwanga unaoakisiwa (angle of reflection, θr) huwa na pembe sawa kulingana na mstari wa wima kwa uso wa kioo (normal line).
- Hii inamaanisha kuwa θi = θr.
- Mwanga unaoingia, mstari wa wima (normal), na mwanga unaoakisiwa wote wako kwenye ndege moja (same plane).
Aina za Kuakisiwa kwa Mwanga
-
Kuakisiwa kwa Nuru Kawaida (Regular Reflection)
- Hutokea kwenye uso laini kama kioo bapa.
- Mwanga unaoakisiwa huunda picha halisi na ya wazi.
- Hutumika kwenye vioo vya kawaida.
-
Kuakisiwa Kusiko na Mpangilio (Diffuse Reflection)
- Hutokea kwenye nyuso mbaya (zisizo laini).
- Mwanga hutawanyika kwa pembe tofauti, hivyo picha haiundwi vizuri.
- Mfano: Ukuta wa chumba, karatasi, au maji yenye mawimbi.
Matumizi ya Kuakisiwa kwa Mwanga katika Kioo Bapa
Kioo bapa (flat glass) hutumika katika maeneo mbalimbali kutokana na sifa zake za kudumu na uwezo wa kuakisi mwanga. Hapa ni baadhi ya matumizi yake:
1. Madirisha na milango ya kioo – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza madirisha na milango katika nyumba, ofisi, na majengo mengine. Hutoa mwangaza wa asili na mtindo wa kisasa.
2. Vioo vya magari – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza vioo vya magari, kama vile vioo vya mbele, vya pembeni, na vya nyuma.
3. Vioo vya samani – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza sehemu za samani kama vile meza, rafu, na vitabu vya sakafuni.
4. Vioo vya mapambo – Hutumika katika mapambo ya nyumba kama vile taa za kioo, milango ya mapambo, na madirisha ya mapambo.
5. Vioo vya kuakisia – Kioo bapa hutumika kutengeneza vioo vya kuakisia (mirrors), ambayo hutumika katika bafu, vioo vya magari, na maeneo mengine.
6. Vioo vya ujenzi wa majengo – Kioo bapa hutumika katika ujenzi wa majengo ya kibiashara au nyumba za kisasa, ambapo hutumika kama sehemu ya kuta za kioo, vilevile kioo cha makadirio ya mwanga.
7.Vyombo vya sayansi kama periskopu na darubini
Matumizi haya yanahitaji kioo bapa kuwa na ubora wa juu na uwezo wa kustahimili shinikizo na hali ya mazingira

















 Join Our Telegram Channel
Join Our Telegram Channel
